Nuffield Health Exeter Hospital
Wonford Rd, Exeter EX2 4UG
Tel: 01392 262 122

Investigations
Jump to:
Common tests for Hand Conditions
It is often possible to make a provisional diagnosis at your first appointment. The history and clinical examination are usually enough to do this. Occasionally, further tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and help your surgeon plan treatment. Below are some of the more common tests performed and some further information about them.
1. X-ray (Radiography)
How it works
X-rays are high-energy
electromagnetic waves
that pass through the
hand onto a detector.
Dense tissues (bones) absorb more, appearing white; softer tissues appear grey-black. The process is quick and painless—often completed in just a few minutes.
Common indications in hand evaluation:
• Fractures or dislocations
• Suspected arthritis (e.g. joint space narrowing, bone spurs)
• Detecting foreign objects or bone tumours
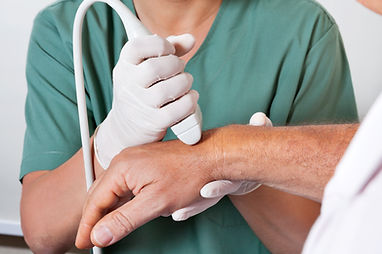
2. Ultrasound (Sonography)
How it works
Ultrasound uses high-frequency
sound waves emitted via a
handheld probe over the skin.
Reflected waves create live images of soft tissues and bone surfaces. It involves no ionising radiation and is widely available and portable.
Common indications for hand conditions:
• Evaluating tendon and ligament tears or inflammation
• Detecting cysts (e.g. ganglion) and soft-tissue masses
• Guiding injections or minor procedures
3. Computed Tomography (CT)
How it works
A rotating X-ray beam and detectors produce multiple 'slices' of the hand. A computer reconstructs these into cross-sectional and 3D images. Can uses contrast dye to enhance vascular or soft-tissue detail.
Common indications in hand disorders:
• Complex or occult fractures
• Pre-surgical planning for bone alignment
• Vascular mapping of hand arteries
• Rapid, detailed imaging in emergencies
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
How it works
MRI uses a strong magnetic
field and radio waves to excite
and detect hydrogen atoms in
the body. It produces highly detailed images, especially of soft tissues, without using ionising radiation.
Common indications for hand imaging:
• Evaluating tendon/ligament injuries
• Detecting occult fractures and bone marrow edema
• Diagnosing inflammatory arthropathies
Comparison Table




Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG)
What are Nerve Conduction Studies?
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are tests used to assess how well your nerves work. They measure how fast and how strong electrical signals travel along a nerve. NCS is often done together with electromyography (EMG) to get a complete picture of nerve and muscle health.
How Do Nerve Conduction
Studies Work?
Small, sticky electrodes are placed
on your skin over the nerve and
muscle being tested. A brief, mild
electrical pulse is delivered to stimulate the nerve. The response is recorded by another electrode to measure how quickly and strongly the nerve sends the signal. You may feel a short tapping or tingling sensation, but it’s generally not painful.
Each test takes only a few minutes, and the whole procedure usually takes 30–60 minutes depending on how many nerves are tested.
Why Are Nerve Conduction Studies Done?
NCS helps diagnose nerve damage or dysfunction. Common reasons include:
Conditions affecting the hands and arms:
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
-
Ulnar Neuropathy
-
Radial Neuropathy
Other uses:
-
Peripheral neuropathy
-
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
-
Brachial plexus injuries
-
Herniated discs affecting nerves
What to Expect
You will sit or lie down comfortably. No needles are used in NCS (needles are used in EMG if it’s performed as well).
You don’t need to fast or change your medication unless told otherwise. If you take any anticoagulants (blood thinning medications) you should let your surgeon know ass these many need to be stopped but only if advised.
Preparation tips:
• Avoid using lotions or oils on your skin on the day of the test.
• Wear loose-fitting clothes that allow access to arms and legs.
• Let your doctor know if you have a pacemaker or implanted electrical devices.
Are Nerve Conduction Studies Safe?
Yes, NCS is very safe. The electrical pulses are very small and pose no risk to your nerves or muscles. You may feel a momentary twitch or tingle, but most people tolerate the test well.
What Do the Results Mean?
NCS results show:
• Speed of nerve signal (conduction velocity)
• Strength of the nerve response (amplitude)
• Delay in signal (latency)
Abnormal results can indicate slowed nerve conduction (due to compression, injury, or disease) or reduced signal strength (which may suggest nerve degeneration or damage).
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Will it hurt?
A: You may feel a short, mild shock or twitch, but it should not be painful.
Q: Is it safe if I’m pregnant?
A: Yes, NCS is safe during pregnancy as it does not use radiation or cause harm to the baby.
Q: Can I go back to work after the test?
A: Absolutely. You can resume normal activities immediately after.
What is Electromyography (EMG)?
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that is often performed alongside nerve conduction studies (NCS) to evaluate the health of muscles and the motor neurons that control them. While NCS measures how well and how fast nerves send signals, EMG assesses how muscles respond to those signals.
During an EMG, a very thin needle electrode is inserted through the skin into a muscle. The electrical activity detected by this needle is displayed on a screen and may be heard through a speaker. This helps the doctor evaluate whether the muscle is receiving proper signals from nerves.
You may feel a small amount of discomfort during the insertion of the needle. The test is usually done in several muscles and takes about 30–60 minutes in total.
EMG is especially helpful for diagnosing:
• Muscle disorders (e.g. muscular dystrophy)
• Diseases affecting the connection between nerves and muscles (e.g. myasthenia gravis)
• Nerve root disorders (e.g. sciatica, cervical radiculopathy)


aboutus
Devon Hand Surgery aims to give you an early diagnosis, rapid treatment (which can often be non-surgical) and perform any necessary surgery when required. We will also supervise your rehabilitation to ensure you have the best chance of restoring function, getting back to work and improving your quality of life.